- +49 176 82095095
- info@ffdpowergermany.de
- Mo. - Fr. : 9:00 - 17:30
As photovoltaic (PV) costs continue to decline, leading to widespread adoption, many areas rich in solar installations are facing grid restrictions on exporting electricity. This shift is steering the solar energy sector towards a future where self-consumption of generated power becomes the norm. For homeowners and businesses alike, producing and consuming your own solar power on-site promises not only greater energy independence but also a direct reduction in energy costs. By harnessing solar energy directly where it’s generated, users can maximize their investment and minimize reliance on fluctuating grid energy prices.
To effectively realize the full potential of photovoltaic self-consumption, integrating a Battery Energy Storage System (BESS) is crucial. Solar power is inherently intermittent—sunlight availability varies throughout the day and with weather conditions, causing fluctuations in power output. BESS serves as a vital buffer in these scenarios, storing excess energy produced during peak sunlight hours and deploying it during overcast periods or peak demand times. This not only stabilizes your power supply but also ensures that none of the valuable solar energy goes to waste, avoiding the need to export excess to the grid or curtail production. With BESS, you can truly capitalize on your solar installations, enhancing both efficiency and sustainability of your energy resources.

FFD POWER’s SOLE series LiFePO4 batteries, seamlessly integrated with solar panels and inverters, offer an optimized self-consumption solution facilitated by meticulous energy analysis and planning. Our system is engineered to meet your specific energy demands while ensuring maximum efficiency—guaranteeing that no generated energy should go to waste.
The SOLE series features flexible capacity options, with AC output ranging from 5kW to 100kW. Equipped with scalable battery storage and advanced energy management systems, FFD POWER empowers homeowners to maximize their energy usage. By storing excess solar energy and minimizing electricity costs, our system promotes complete self-consumption of all energy produced, aligning with sustainable living practices and financial savings.
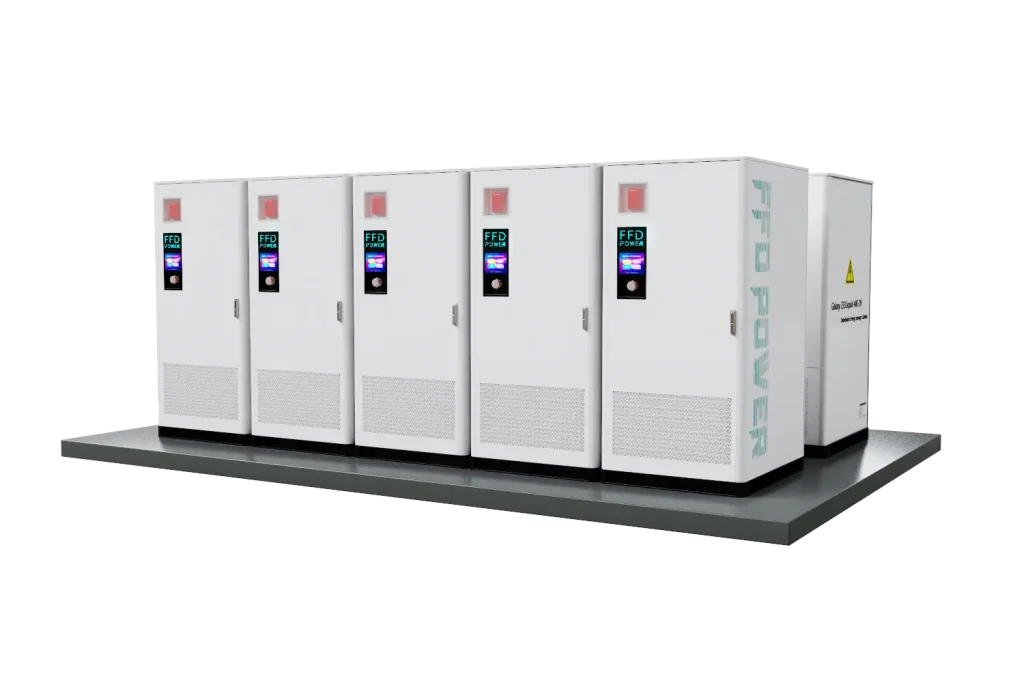

FFD Power’s Cabinet Battery Energy Storage System (BESS) stands at the forefront of self-consumption energy management solutions. Featuring a nominal output of 125 kW and 233 kWh per battery cabinet, our modular system can effortlessly expand up to 7 MWh. This scalability is ideal for adapting to the shifting regulatory landscape regarding renewable energy contributions to the grid.
Furthermore, the Cabinet BESS provides flexibility in energy storage. Equipped with an advanced Energy Management System (EMS), it enables businesses to cultivate renewable energy as a reliable power source to reduce their carbon footprint without the concern of penalties for exporting excess power during peak production times. With less reducing output or wasting energy, our BESS solution makes it a smart choice for businesses aiming to optimize their energy strategies and enhance sustainability.
In regions with abundant PV installations which usually results in low utility rates during peak sunlight hours, a common strategy is to harness and store solar energy with BESS for later use when utility rates are higher. This method not only capitalizes on the natural availability of solar power but also aligns with financial incentives to reduce energy costs during peak tariff periods.
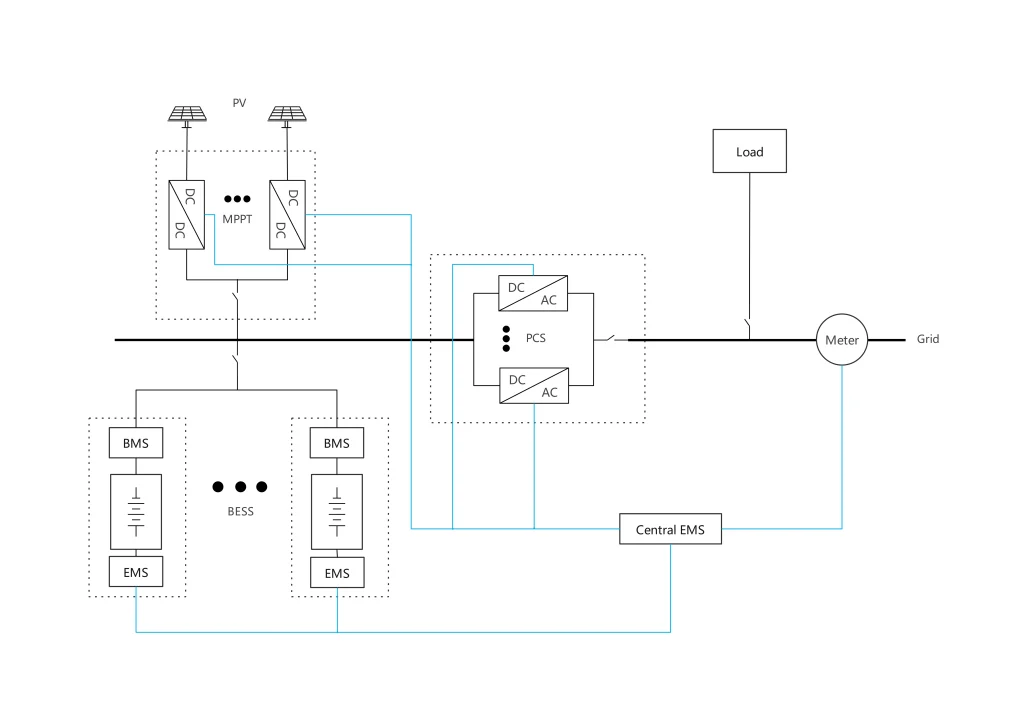
In maximizing the efficiency of solar power usage, DC-coupling the photovoltaic (PV) panels with battery storage systems emerges as a highly effective approach. This setup enhances the overall energy efficiency of the system, ensuring that more of the solar power generated is directly stored and later used, rather than lost in the energy conversion process. It is most suitable for use cases that need to store the majority of the energy generated by the PV system.
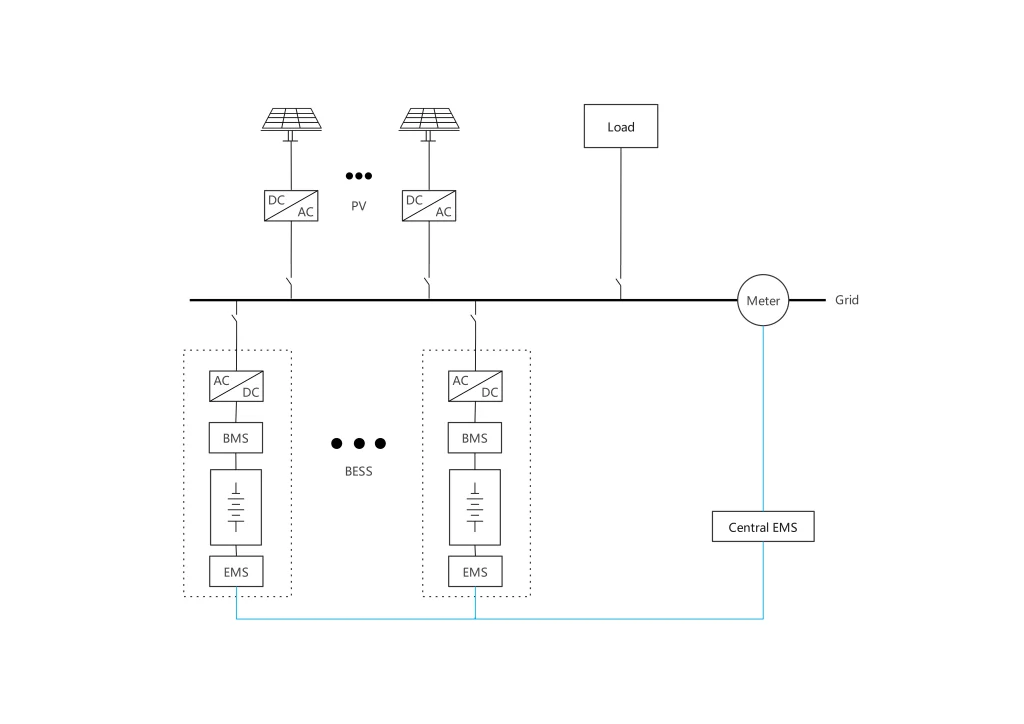
For large-scale photovoltaic (PV) deployments, there are specific requirements for flexibility and scalability in energy storage, and AC-coupling systems are perfectly suited to meet these needs. Moreover, such systems generally support substantial load demands, with the majority of solar energy being utilized immediately upon generation. Only a portion of the electricity produced during peak generation periods needs to be stored.
Furthermore, during the day, when industrial and commercial peak electricity prices coincide with high solar output, the most efficient strategy is to consume as much of the AC-side output from the PV system as possible. This approach is particularly well-suited for commercial and industrial settings with large loads where minimal energy storage is necessary. This system strategy capitalizes on real-time energy production and consumption, optimizing energy usage and cost-efficiency during periods of high demand.
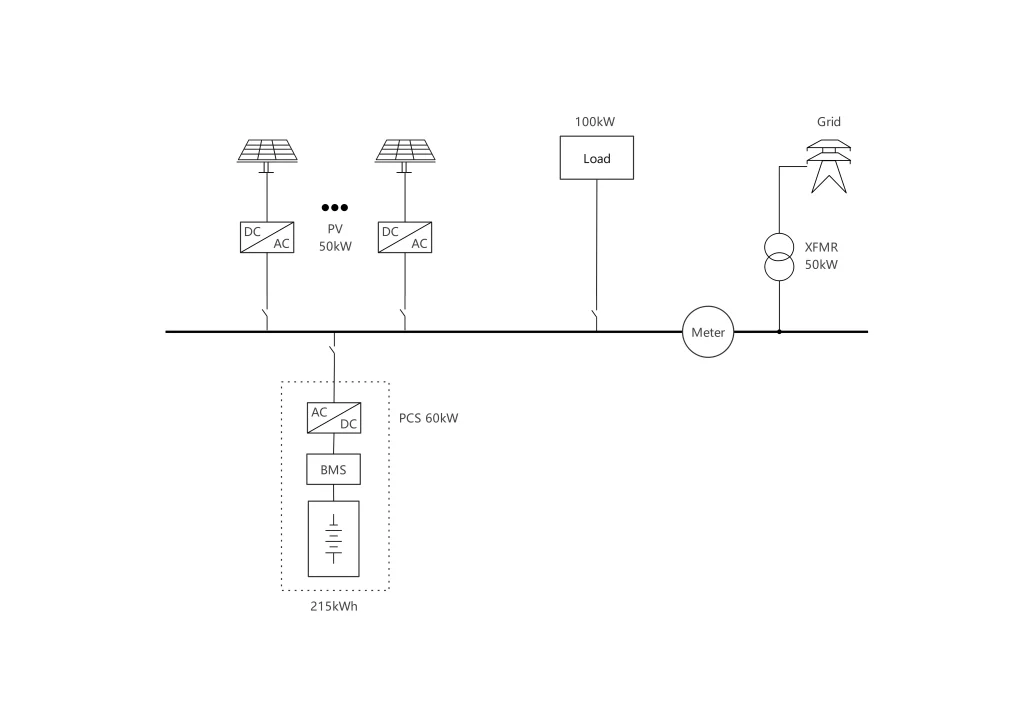
60kW / 215kWh BESS with 50kWp Photovoltaic System for a 100kW Load Operating 6 Hours Daily in Haarlem, the Netherlands
In this scenario, the 50kWp photovoltaic (PV) system directly powers a 100kW load operating at full capacity for 6 hours during daylight. Notably, there’s a grid restriction of 50kW, and exporting excess energy back to the grid incurs penalties. Therefore, immediate consumption of the generated solar power is both mandatory and optimal given the system’s constraints and load requirements.
Given the circumstances, an AC coupling method is ideal for this PV system. With a peak capacity of only 50kWp against a 100kW load, the system inherently lacks surplus energy for storage. However, the grid’s 50kW supply limit and the operational requirement of 6 hours daily necessitate the use of a Battery Energy Storage System (BESS).
The BESS will charge from the grid during off-peak hours and discharge during peak daylight hours to support the load. This is crucial because the PV system alone cannot consistently deliver the full 50kW needed to complement the grid’s maximum supply of 50kW, particularly under Haarlem’s average sunlight conditions, which equate to only about 2.5 hours of peak output. This results in approximately 3.5 hours of energy deficit each day that the BESS needs to compensate for, ensuring smooth and uninterrupted operation. Thus, the combination of the PV system with BESS not only ensures compliance with grid limitations but also maximizes energy efficiency, guaranteeing that the system meets the daily operational demands efficiently and sustainably.

WhatsApp us